Key points of daily maintenance for CNG fuel gas vehicles
The routine maintenance of CNG (compressed natural gas) vehicles not only affects the vehicle's power performance but also directly impacts its safety in use. Due to its fuel characteristics (high pressure, gas combustion) and system structure (gas supply, pressure relief device, etc.), which differ from traditional fuel vehicles, maintenance should focus on the following aspects:
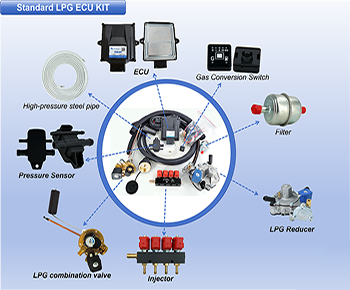
I. Gas supply system: core safety and performance guarantee
1. Maintenance of gas cylinders and accessories
- Regular inspection: CNG cylinders are high-pressure vessels and must be inspected regularly at qualified institutions in accordance with national regulations. Overdue use is strictly prohibited.
- Regular inspection: During each refueling or maintenance session, inspect the cylinder's mounting bracket and bolts for any signs of looseness or corrosion, to prevent the cylinder from shaking or falling off while the vehicle is in motion (especially after driving over bumpy roads).
- Appearance inspection: Observe the surface of the cylinder for any scratches, corrosion, or deformation, and check the integrity of the cylinder valve (stop valve). If there is any damage, it must be replaced immediately, and unauthorized disassembly is prohibited.
2. Piping and connectors: Leak prevention is key
- Leakage investigation: Regularly (it is recommended to do so monthly) apply soap water to gas pipeline joints, gas filling ports, pressure reducing regulator interfaces, and other relevant areas, and observe whether there are bubbles emerging (a leak will have a distinct gas odor, requiring immediate vehicle shutdown for inspection). If a leak is detected, it is strictly prohibited to use an open flame. Close the cylinder valve and contact a professional for maintenance.
- Pipe protection: Avoid bumping or squeezing the pipes (such as chassis scratching), to prevent deformation or cracking of the pipes; check the aging condition of the pipes (especially rubber pipes, which need to be replaced in a timely manner if they become hardened or cracked).
- Gas filling port cleaning: Before gas filling, wipe away dust and impurities from the gas filling port to prevent foreign objects from entering the pipeline; after gas filling, ensure that the gas filling valve is closed properly to prevent minor leaks.
3. Pressure reducing regulator and filter
- Pressure reducing regulator: It is a core component that reduces high-pressure gas (20MPa) to a low pressure suitable for engines (0.1-0.2MPa). It requires regular inspection by professionals (recommended every 20,000 kilometers or 1 year):
- Check if there is any oil stain or impurity blockage inside (which may affect the decompression efficiency and lead to insufficient gas supply);
- Check whether the diaphragm and valve are worn (if there is air leakage or unstable pressure reduction, replace the components);
- Gas filter: It filters out moisture and dust from the gas. It is recommended to replace it every 10,000 to 20,000 kilometers to avoid blockage and subsequent decrease in gas supply.

II. Ignition system: Adapted to gas combustion characteristics, CNG has a higher combustion temperature (about 2000¡æ) than gasoline (about 1500¡æ), which causes greater wear and tear on the ignition system and requires special maintenance:
- Spark plug: It is recommended to check it every 20,000-30,000 kilometers. If the electrode is worn (gap is too large) or there is severe carbon buildup, it needs to be replaced promptly. It is advisable to choose a CNG-specific spark plug (high temperature resistant, electrode wear-resistant type) to avoid using ordinary gasoline spark plugs (which are prone to ablation).
- Ignition coil: Regularly check whether the coil wiring is loose. If there is ignition delay or power fluctuation, it may be due to coil aging (insufficient output voltage), and timely maintenance or replacement is required.
III. Intake and mixing system, ensuring combustion efficiency
- Air filter: Clean it every 5,000-10,000 kilometers and replace it every 20,000 kilometers. If it is clogged, it will lead to insufficient air intake, resulting in an excessively rich mixture of gas and air (incomplete combustion, reduced power, and unstable idle speed).
- Mixer (or electronically controlled air injection device): - Mechanical mixer: Regularly check for any blockages or wear, and calibrate the mixture ratio if necessary (both too rich and too lean can affect power output, and too rich may also cause "backfire" in the exhaust pipe).
- Electronically controlled CNG system: Check whether the gas injection quantity is normal and whether the data from the oxygen sensor and pressure sensor are accurate through a diagnostic tool, to avoid gas supply imbalance caused by abnormal signals.
IV. Engine and related components: Reducing carbon buildup and wear
- Carbon deposit removal: CNG burns cleaner, but long-term use may still lead to the formation of carbon deposits on the valves and intake ports (especially during low-speed driving). It is recommended to clean the intake ports and valves with professional equipment every 30,000 to 50,000 kilometers, or add fuel additives when using gasoline (for dual-fuel vehicles) to reduce carbon buildup.
- Oil and lubrication: CNG combustion has no oil dilution effect and involves high temperatures. It is recommended to use high-temperature resistant and oxidation-resistant synthetic oil, shorten the oil change interval (500-1000 kilometers earlier than for gasoline vehicles), and avoid poor lubrication caused by rapid aging of the oil.
- Cylinder tightness: Regularly check the cylinder pressure (especially for vehicles that have been in use for more than 3 years). If the piston ring or valve oil seal is worn, resulting in insufficient pressure, it will significantly reduce power and require timely maintenance.
V. Electronic control system: avoid interference from fault codes
- If the vehicle is equipped with a CNG electronic control unit (ECU), it is recommended to use a dedicated diagnostic tool to conduct a test every six months and clear any fault codes (such as sensor false alarms, abnormal gas supply, etc.), to ensure that the system operates with optimal parameters.
- Avoid unauthorized modification of the gas system (such as increasing the gas supply to "boost power"), which may lead to engine overload, excessive emissions, and even malfunction.

VI. Daily usage habits: Reduce unnecessary wear and tear
- Do not fill the cylinder too full (usually to 80%-90% of the rated pressure) to avoid excessive pressure due to temperature rise (especially in summer).
- When starting a dual-fuel vehicle, it is recommended to warm up the vehicle with gasoline first (for 30 seconds to 1 minute), and then switch to CNG once the engine temperature has risen, in order to reduce wear during cold starts.
- When CNG is not used for a long time, a small amount of gas (pressure ¡Ý 0.5 MPa) should be kept in the cylinder to prevent moisture from entering the pipeline and causing corrosion.
- If you detect any abnormalities such as gas odor, sudden power loss, or unstable idle speed, immediately close the cylinder valve, stop the vehicle for inspection, and do not continue driving.
The core of daily maintenance for CNG (compressed natural gas) vehicles lies in "safety first, prevention foremost": particular emphasis should be placed on the sealing and safety of the high-pressure system (including gas cylinders, pipelines, and pressure relief devices). Meanwhile, combustion efficiency should be maintained through regular maintenance of the ignition and intake systems. It is recommended to seek professional maintenance from institutions with CNG repair qualifications to avoid potential safety hazards or performance degradation caused by improper operation.
Refer to:https://www.acko.com/car-guide/cng-car-maintenance-and-safety-guide/
The pictures and articles are from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete them.
Popular articles
-

How the CNG Automotive S
Compressed natural gas (CNG) automotive systems
-

What Is CNG Pressure Red
The pressure reducer of natural gas vehicle is
-

Advantages Of CNG Gas V
Compressed natural gas vehicles are vehicles th
-

Reasons For High Gas Con
1. Original vehicle condition A. The tec
-

Differences Between Sing
Characteristics of Gas Single Point Device
-

How To Improve The Power
1. Install ignition advance angle What i
-

Advantages And Principle
LPG and CNG are two mainstream alternati
-

How The CNG Gas Vehicle
If you want to know ¨C how does the CNG conversi






Latest comments
0piece comment
no comments, welcome to comment¡£